It’s a fear many parents with children on the autism spectrum say they live with every day: that their child will bolt out the door at any second and head straight to the nearest body of water, drawn to it as if by some powerful magnetic force.
The behavior is known as wandering, or eloping, and it’s something that parents of nearly half of children with autism say they’ve experienced. Many of these children exhibit a diminished sense of fear, making a beeline to things they’re attracted to that could place them in harm’s way – most often natural bodies of water like ponds, creeks or drainage ditches – but also highways, trains, construction equipment, firetrucks or even roadway signs.
Over a 10-year period, 1,516 children with autism were reported missing to the National Center for Missing & Exploited Children (NCMEC). Of those, 64 children were recovered deceased with drowning the leading cause of death. Sadly, the number is likely much higher because children who wander often reach water before they can be reported missing and their deaths are not distinguished from other accidental drownings. Kids on the autism spectrum are 160 times more likely to die from drowning compared to the general population of children, according to the American Journal of Public Health.
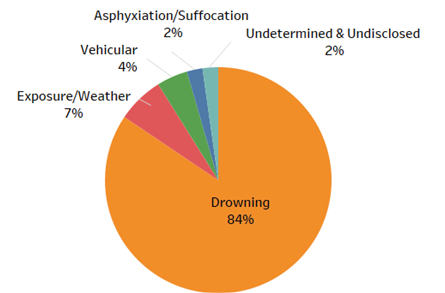
NCMEC’s 10-year analysis, from 2011 to 2020, shows causes of accidental deaths after children wander from safe environments.
Parents use all kinds of strategies and technologies to keep their children safe – sensors to detect when a door is opened, enlisting help from neighbors, cameras, special locks, tracking devices. Now that Covid-19 restrictions are lifting, parents have another potential lifeline: swimming lessons.
Before the pandemic, the YMCA was teaching swimming to children with disabilities as part of a pilot program. Now, with pools opening back up, the organization is bolstering its inclusive swimming program, providing instructors with more training and giving them the tools they need to work with children who may be nonverbal or have difficulty communicating.
“As communities across the country reopen, we want to remind everyone that water safety isn’t just fun – it’s essential,” said Lindsay Mondick, director of innovative priorities at Y-USA. “The Y’s classes provide a safe, fun and healthy environment for children with disabilities to learn important water safety skills in a way that can ultimately save their lives if ever faced with an unexpected situation with water.”
Each child on the autism spectrum is unique, so the YMCA has been working with parents to meet their individual needs, Mondick said. Some want private lessons for their children, while others believe their kids would benefit from swimming classes with their peers, she said.
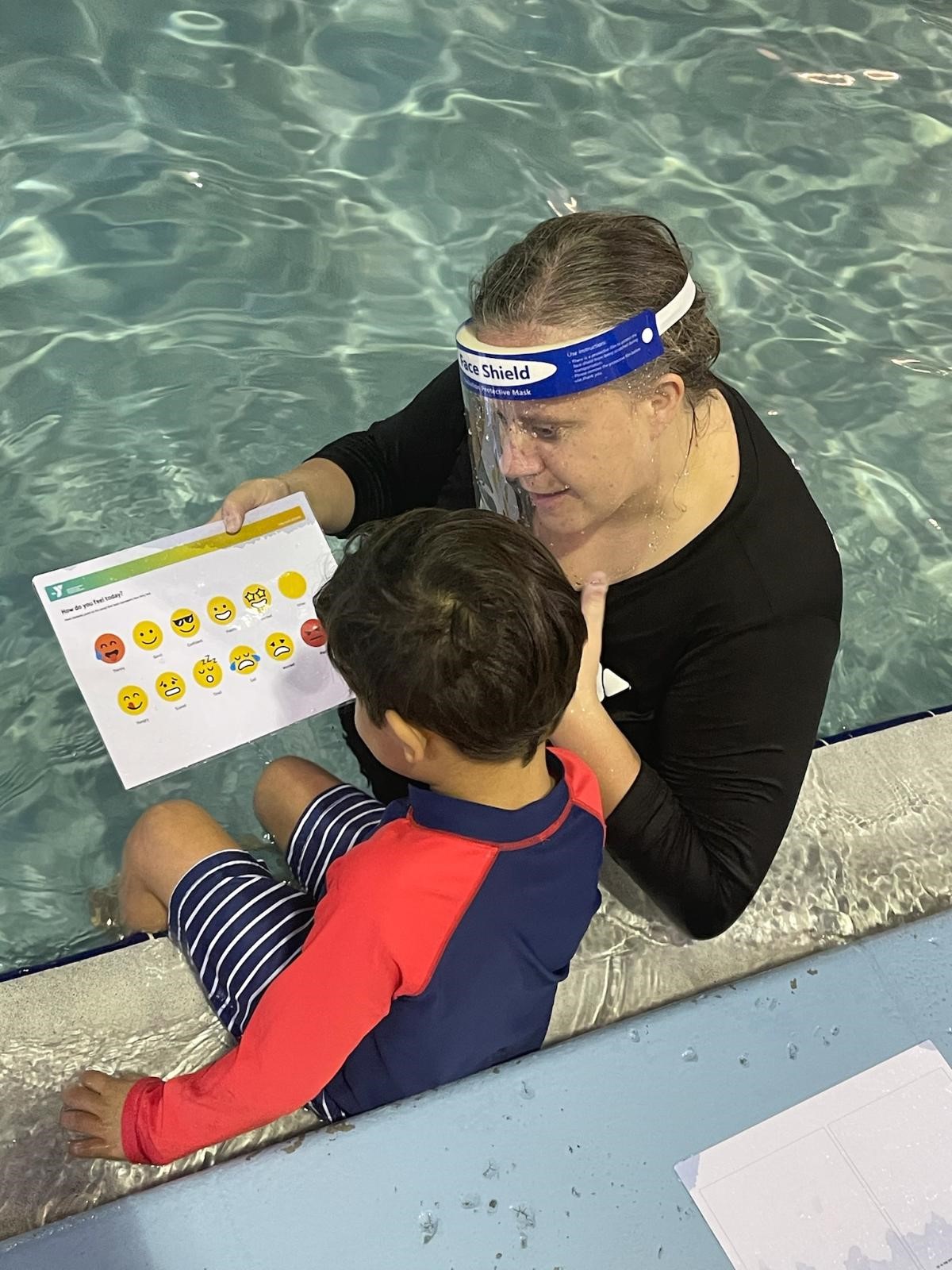

Child is taught swimming lessons at YMCA using visual aids.
The National Autism Association (NAA) has been working with the organization since 2012 and has a list of Y’s that offer inclusive classes on its website, https://nationalautismassociation.org/resources/autism-safety-facts/swimming-instructions/. Other organizations, including the Red Cross, offer classes, and the NAA tells parents to Google “swimming lessons and special needs” if they don’t have a Y in their community.
“We recommend swimming lessons as one of the first safeguards parents should get for their children, a pretty critical piece,” said Lori McIIwain, co-founder of the NAA and mother of a son with autism. “It’s one layer.”
Parents interested in swimming lessons with Red Cross-trained instructors should contact their local parks and recreation departments, said Connie Harvey, director of Aquatics Centennial Initiatives. The Red Cross offers lessons at 3,500 aquatic facilities throughout the United States, she said.
The need for swimming lessons for children on the autism spectrum is growing as the number of children diagnosed with autism continues to grow. Today, one in 54 children in the United States are on the autism spectrum, compared to one in 68 in 2014, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
McIIwain said her organization encourages parents to have their children take at least one swimming lesson while wearing their clothes and shoes as would be the case if they wandered to a body of water. The NAA tracks wandering cases and counts about 20 a month, including two to three deaths, often learning about them when a parent calls to report their child drowned after wandering.
When parents say swimming lessons wouldn’t work for their child because he or she doesn’t like water, including taking showers and brushing their teeth, McIIwain says her organization encourages them to get swimming lessons anyway. Children who don’t like water may still be attracted to bodies of water in natural settings, and there are strategies to ease them into swimming lessons, she said.
Mondick says sometimes just teaching these children that they must ask for permission before ever getting in the water can be a lifesaver. The NAA agrees and encourages parents to put water play on a visual schedule for their children so they have a structured routine.
“It’s actually really simple, but it works,” McIIwain said.
For more information, visit: https://www.missingkids.org/theissues/autism. For our next NCMEC autism training class for law enforcement, visit: https://connect.missingkids.org.
RED CROSS - TAKE A CLASS (English
OR
RED CROSS - TAKE A CLASS (Spanish)






No comments:
Post a Comment